This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Policy Brief (Issue 1): Economic Evaluation of the Implementation of the WHO Package of Essential Non-Communicable Disease (PEN) Interventions in Indonesia
Details
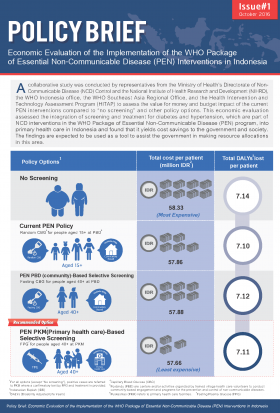
A collaborative study was conducted by representatives from the Ministry of Health’s Directorate of Non – Communicable Disease (NCD) Control and the National Institute of Health Research and Development (NIHRD), the WHO Indonesia office, the WHO Southeast Asia Regional Office, and the Health Intervention and Technology Assessment Program (HITAP) to assess the value for money and budget impact of the current PEN interventions compared to “no screening” and other policy options. This economic evaluation assessed the integration of screening and treatment for diabetes and hypertension, which are part of NCD interventions in the WHO Package of Essential Non-Communicable Disease (PEN) program, into primary health care in Indonesia and found that it yields cost savings to the government and society. The findings are expected to be used as a tool to assist the government in making resource allocations in this area.




